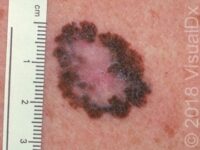
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the second most common form of skin cancer. Squamous cell carcinoma usually occurs on sun-damaged skin, especially in light-skinned individuals with a long history of chronic sun exposure.
Squamous cell carcinoma requires treatment to prevent it from becoming too invasive. If it is caught early and treated appropriately, squamous cell carcinoma rarely spreads (metastasizes) to lymph nodes or to internal organs. However, if it is neglected, squamous cell carcinoma can cause tissue destruction or it may spread internally, causing serious health problems and even death.
Who's At Risk?
Although squamous cell carcinoma can be found worldwide, it is most commonly seen in elderly, light-skinned people with a large amount of sun exposure.
Risk factors for the development of squamous cell carcinoma include:
- Age over 50 years
- Light skin, light hair, or light eyes
- Male sex
- Chronic exposure to sunlight or other ultraviolet light
- Exposure to certain chemicals, such as arsenic or tar
- Exposure to radiation, such as X-ray treatment for internal cancers
- Long-term suppression of the immune system, such as organ transplant recipients
- Long-term presence of scars, such as from a gasoline burn
- Chronic ulcers
- Previous skin cancer
Darker-skinned people are much less likely to develop squamous cell carcinoma, though it is the most common form of skin cancer in people of African and Asian descent.
Signs & Symptoms
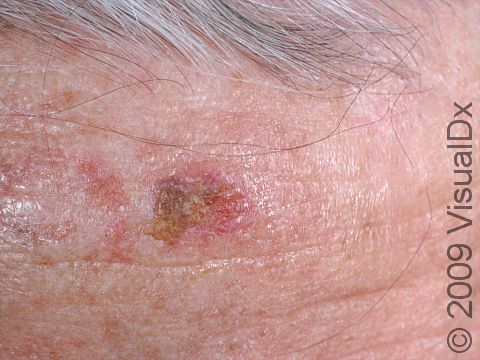
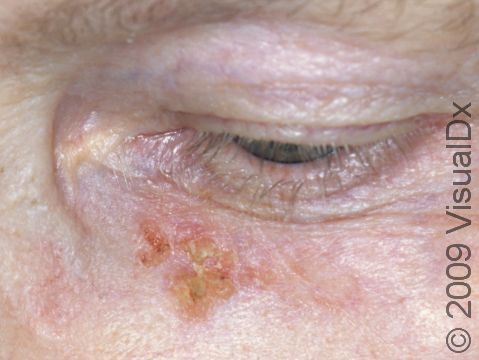
The most common locations for squamous cell carcinoma in light-skinned individuals include:
- Head and neck
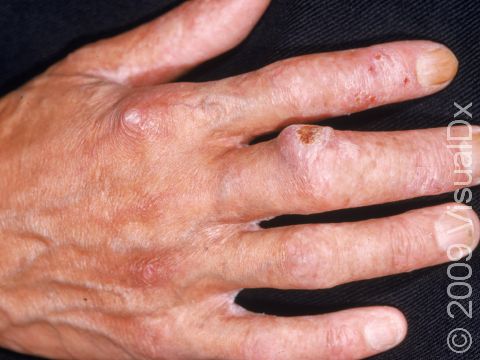
- Arms and hands
- Shoulders
- Back
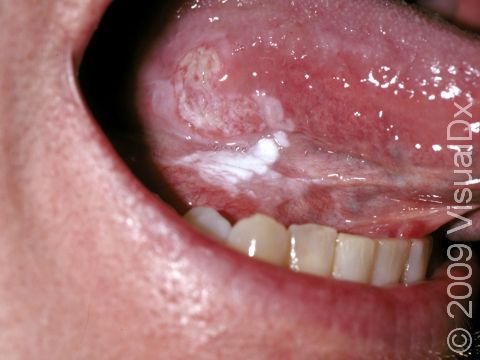
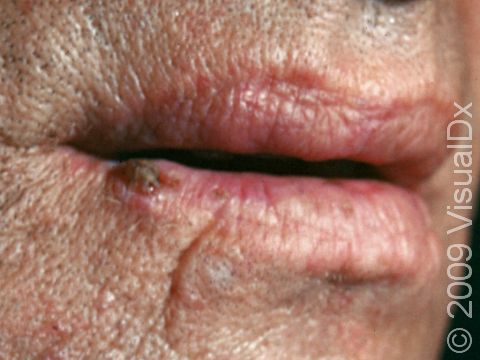
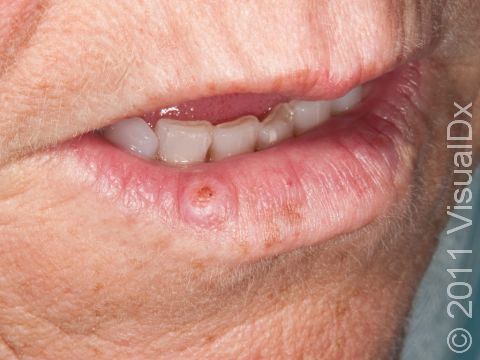
- Lower lip, especially in smokers
In people with darker skin, the most common locations for squamous cell carcinoma include:
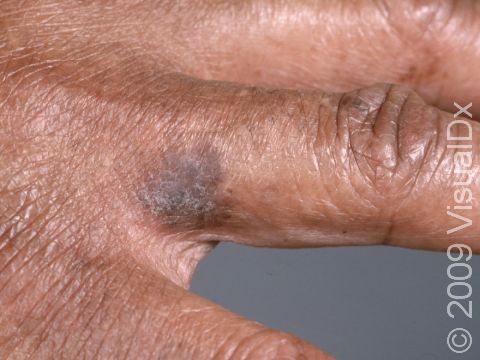
- Legs
- Non-sun-exposed sites
- Sites of chronic scarring
- Non-healed leg ulcers
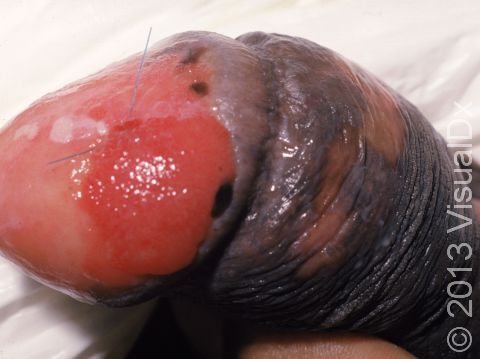
- Anus
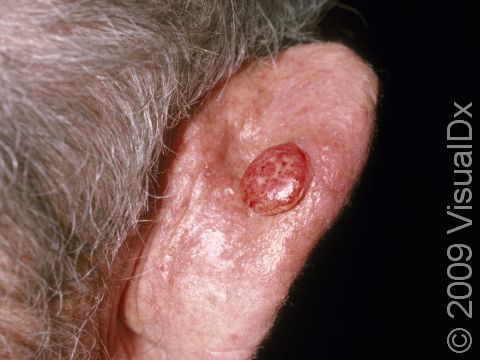
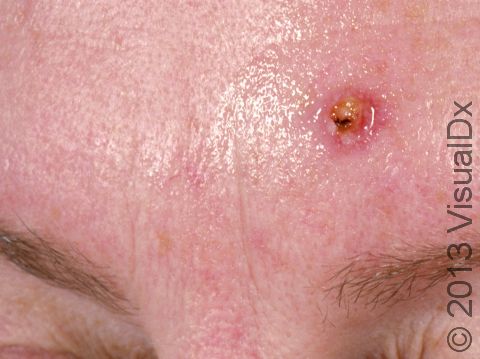
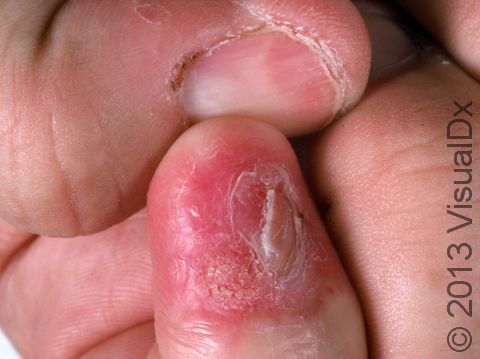
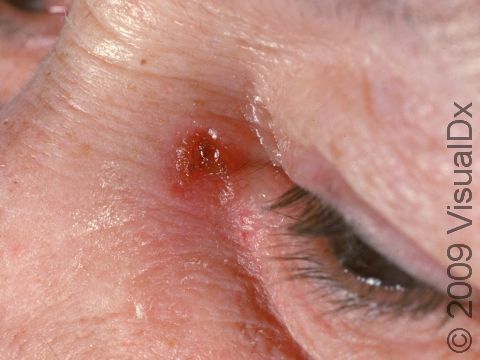
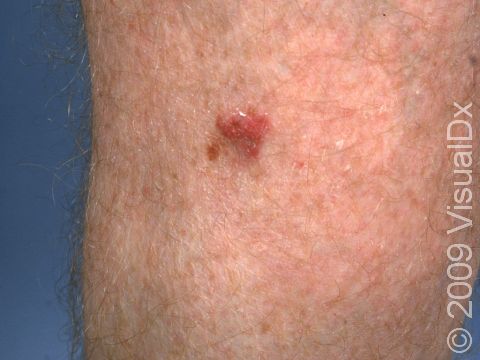
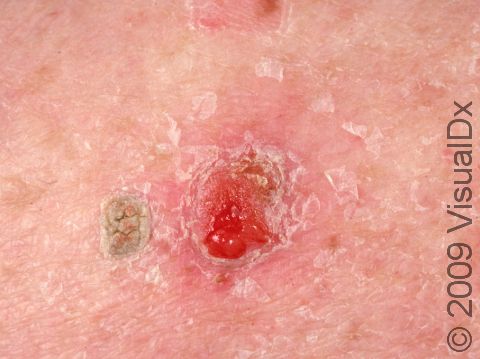
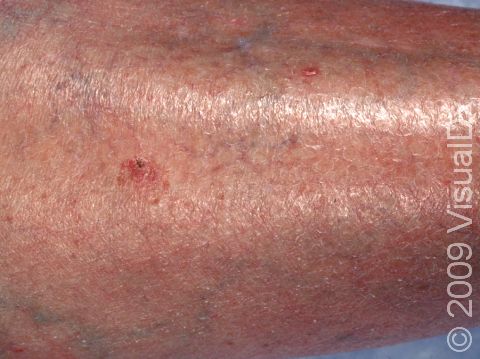
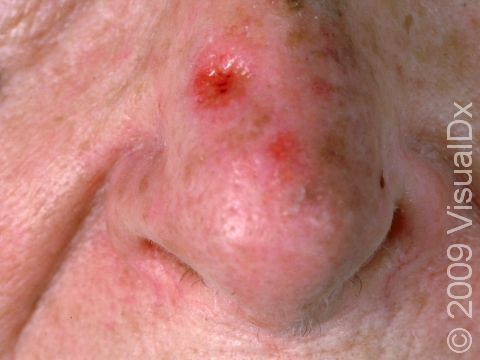
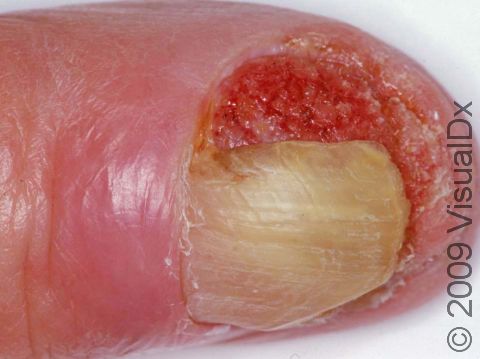
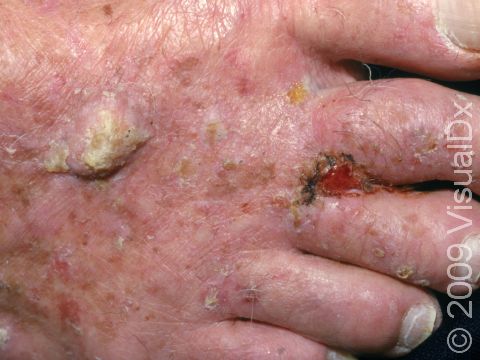
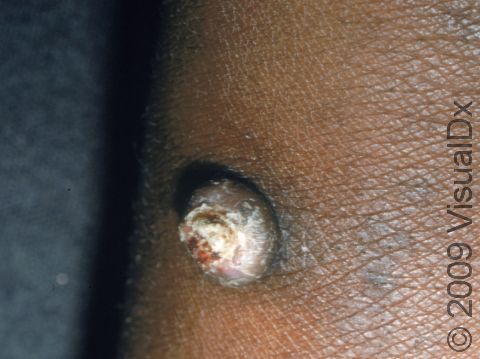
Early squamous cell carcinoma appears as a small, pink to red, scaly spot. Over time, the lesion becomes a larger and deeper bump. Eventually, the center of the squamous cell carcinoma becomes ulcerated and may bleed or become scabbed over.
Early squamous cell carcinomas do not typically have any symptoms, but larger lesions may be tender or may bleed.
Self-Care Guidelines
Preventing sun damage is crucial to avoiding the development of squamous cell carcinoma:
- Avoid ultraviolet light exposure from natural sunlight or from artificial tanning devices.
- Wear broad-spectrum sunscreens (blocking both UVA and UVB) with SPF 30 or higher, reapplying frequently.
- Wear wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeved shirts.
- Stay out of the sun in the middle of the day (between 10:00 AM and 3:00 PM)
If you have a new bump on sun-exposed skin or a non-healing sore on any part of your body, you should see your primary care provider or a dermatologist as soon as possible. There are no effective self-care treatment options for squamous cell carcinoma.
Once a month, you should perform a self-exam to look for signs of skin cancer. It is best to perform the exam in a well-lit area after a shower or bath. Use a full-length mirror with the added assistance of a hand mirror when necessary. Using a hair dryer can help you examine any areas of skin covered by hair, such as your scalp.
- In front of a full-length mirror, inspect the front of your body making sure to look at the front of your neck, chest (including under breasts), legs, and genitals.
- With your arms raised, inspect both sides of your body making sure to examine your underarms.
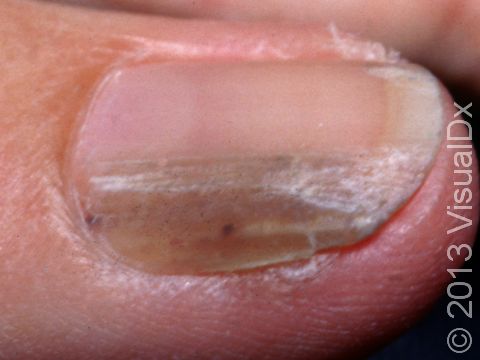
- With your elbows bent, examine the front and back of your arms as well as your elbows, hands, fingers, area between your fingers, and fingernails.
- Inspect the tops and bottoms of your feet, the area between your toes, and toenails.
- With your back to the mirror and holding a hand mirror, inspect the back of your body, including the back of your neck, shoulders, legs, and buttocks.
- Using a hand mirror, examine your scalp and face.
As you perform your monthly self-exam, familiarize yourself with the moles, freckles, and other marks on your body, and look for any changes in them from month to month, including shape, size, color, or other changes, such as bleeding or itching.
Treatments
If your physician suspects squamous cell carcinoma, he or she will first want to establish the correct diagnosis by performing a biopsy of the lesion. The procedure involves:
- Numbing the skin with an injectable anesthetic.
- Sampling a small piece of skin by using a flexible razor blade, a scalpel, or a tiny cookie cutter (called a “punch biopsy”). If a punch biopsy is taken, a suture (stitches) or two may be placed and will need to be removed 6–14 days later.
- Having the skin sample examined under the microscope by a specially trained physician (dermatopathologist).
If caught early and treated appropriately, squamous cell carcinomas generally have a good prognosis. Treatment of a biopsy-proven squamous cell carcinoma depends upon many factors, including its microscopic appearance, its size and depth, its location on the face or body, and the general health of the patient. In general, the following treatment options exist for squamous cell carcinoma:
- Cryosurgery with liquid nitrogen – Very cold liquid nitrogen is sprayed on the lesion, freezing it and destroying it in the process. This is a good option for low-risk squamous cell carcinomas.
- Electrodesiccation and curettage, also known as “scrape and burn” – After numbing the lesion, the doctor uses a curette to “scrape” the skin cancer cells away, followed by an electric needle to “burn,” or cauterize, the tissue. The electrodesiccation helps to kill the cancer cells and also to staunch any bleeding of the site. This is a good option for low-risk squamous cell carcinomas.
- Excision – The squamous cell carcinoma is cut out with a scalpel, and stitches are usually placed to bring the wound edges together. This is a good option for low-risk and some high-risk squamous cell carcinomas.
- Mohs micrographic surgery – In this technique, the physician takes tiny slivers of skin from the cancer site until it is completely removed. This technique is particularly useful for high-risk squamous cell carcinomas and for lesions located on the nose, the ears, the lips, and the hands.
- Radiation treatment – X-ray therapy is often useful for patients who are not good surgical candidates because of other health issues.
Rarely, the squamous cell carcinoma may spread internally (metastasize). Squamous cell carcinomas that develop in scars, on the lip, and on the ear have the highest risk of spreading. Lymph nodes may need to be examined for the presence of SCC. If internal spread is suspected, referral to an oncologist (a physician specializing in cancer treatment) for possible chemotherapy or other treatments would be appropriate.
Finally, it is important to remember that treatment of squamous cell carcinoma is not complete once the skin cancer has been removed. Frequent follow-up appointments with a dermatologist or with a physician trained to examine the skin are essential to ensure that the SCC has not recurred and that a new skin cancer has not developed. In addition, good sun protection habits (see Self-Care) are vital to preventing further ultraviolet light damage.
Visit Urgency
If you have developed a new bump on sun-exposed skin, or if you have a spot that bleeds easily or does not seem to be healing, then you should make an appointment with your primary care physician or with a dermatologist. You should also make an appointment if an existing spot changes size, shape, color, or texture, or if it starts to itch, bleed, or become tender.
Try to remember to tell your doctor when you first noticed the lesion and what symptoms, if any, it may have (such as easy bleeding or itching). Also be sure to ask your parents, siblings, and adult children whether or not they have ever been diagnosed with skin cancer, and relay this information to your physician.
Trusted Links
References
Bolognia, Jean L., ed. Dermatology, pp.1674-1693. New York: Mosby, 2003.
Freedberg, Irwin M., ed. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 6th ed. pp.737-743. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003.
Last modified on February 10th, 2023 at 6:57 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder