Salmonellosis
Salmonella is the name for a family of bacteria that cause diarrheal illness in humans. Salmonella is most commonly thought of as the bacteria that lives on raw poultry, and while this is true, it is also found on raw beef, milk, eggs, and even fruits and vegetables. It can be spread directly from the contaminated food or from fecal contact with an infected person. Salmonella bacteria are the type of bacteria that cause “food poisoning” (ie, a fever, vomiting, and diarrheal illness caused by contaminated food). This type of “food poisoning” is more properly called salmonellosis. Salmonella Typhi is a type of Salmonella that causes typhoid fever; this is also includes fever, vomiting, and often diarrheal illness, but it is much more severe that salmonellosis. Salmonella can also be spread from animals to humans; reptiles (including pet turtles) and chicks and ducklings (even those that look well and are not sick) can spread Salmonella and cause salmonellosis in humans.
How do I get Salmonella?
- By eating or drinking foods contaminated with Salmonella, usually raw or undercooked poultry or beef, raw milk, raw eggs, or contaminated fruits and vegetables.
- By handling certain animals, such as reptiles (including pet turtles), chicks, or ducklings.
Who's At Risk?
Anyone who comes into contact with Salmonella-infected foods may develop symptoms of vomiting and diarrhea; the very young, very old, and those who have a compromised immune system are at much higher risk of developing more serious complications from salmonellosis, such as bacteria in the blood stream (sepsis) and death.
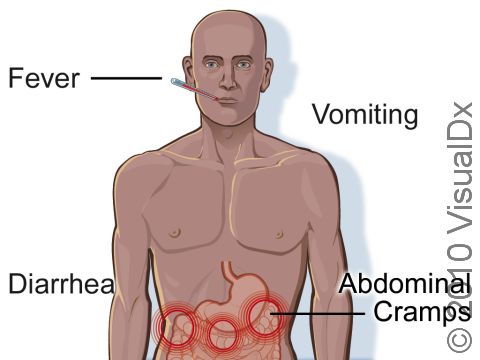
Signs & Symptoms
Symptoms of salmonellosis include the following:
- Fever
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps
- Vomiting
These symptoms start within hours to days of ingesting the contaminated food and usually last for about a week.
Self-Care Guidelines
Stay hydrated, preferably with a liquid that contains some sugar and electrolytes, such as a sports drink. Drink at least 2 liters of liquid a day. Eat a bland (not spicy) low-fat diet. Avoid milk and dairy products until the diarrhea improves. Practice good hand hygiene, as the bacteria can easily be spread from one person to another through fecal contamination.
Treatments
Some Salmonella infections do not necessarily need to be treated, so your doctor may not prescribe anything. Typhoid and paratyphoid fever (caused by S. Typhi and S. Paratyphi) are usually treated with antibiotics. Your doctor may test a sample of your stool for cells and bacteria, and he/she may choose to prescribe an antibiotic based on this test. There is no vaccine available for the types of Salmonella that cause salmonellosis. There is a vaccine available for S. Typhi, however, the bacterium that causes typhoid fever.
Visit Urgency
If the diarrhea becomes bloody or lasts longer than a few days, or if you develop a high fever, see your doctor. If you experience signs of dehydration, such as dizziness or fainting, or if you have mental confusion, see a doctor immediately.
Last modified on October 6th, 2022 at 2:48 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder