Gonorrhea, Primary Infection
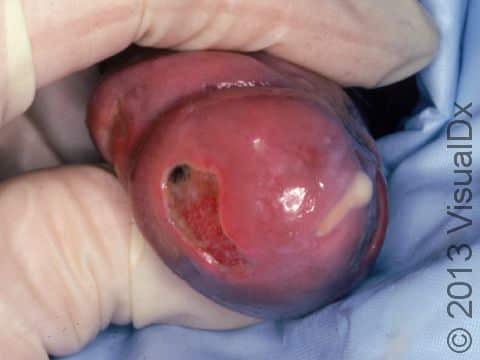
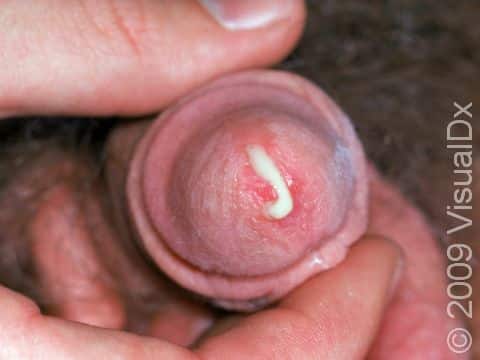
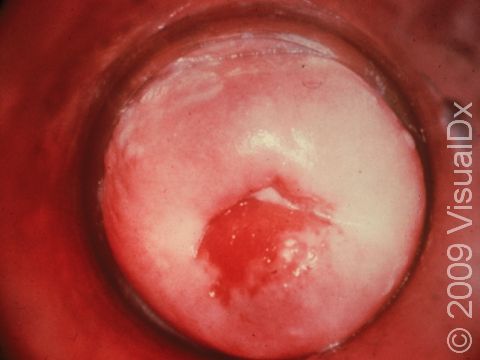
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhea. It is a contagious sexually transmitted disease spread by unprotected oral, vaginal, or anal sex with an infected partner. The bacterium can live in the mouth, semen or vaginal fluids of infected persons. It is possible to be infected without symptoms and continue to spread the disease.
If the infection is not treated, it can spread to other parts of the body, including the throat, joints, and eyes (potentially leading to blindness). Complications from gonorrhea infection include pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can affect fertility in women; inflammation of the testicles (epididymitis), which can lead to infertility in men; blindness in an infant infected during delivery; and widespread infection with a fever, rash, and joint pain.
Who's At Risk?
Anyone who is sexually active is at risk for gonorrhea as well as other sexually transmitted diseases. Teens and young adults are at the highest risk for contracting gonorrhea; in the US, 75% of cases occur in those under 30 years old. Since there is no immunity developed in infection with gonorrhea, the infection can be acquired again if there is sexual contact with an infected person.
Signs & Symptoms
There may be no symptoms associated with gonorrhea, particularly in women.
Infection often starts with only mild symptoms of discomfort with urination. Later there may be frequent and painful urination or defecation; a thick, cloudy, or bloody discharge from the penis, vagina, or rectum; or pain with sexual intercourse. Throat infection may present a sore throat only.
Occasionally, the infection can spread throughout the body and presents with symptoms of fever, chills, swollen or painful joints, and small bumps that may be red or purple on the hands or feet. This is referred to as the arthritis-dermatitis syndrome.
Self-Care Guidelines
Gonorrhea is highly contagious and can have many serious side effects if left untreated. If you are sexually active and suspect you have been exposed to gonorrhea, you should seek medical care immediately. You should avoid any further sexual activity and notify any previous sexual partners.
Gonorrhea can be prevented by abstaining from casual sexual activity and using condoms correctly during any sexual contact. If you are in a long-term relationship, make sure that you know your partner’s sexual history or ask that your partner is tested prior to engaging in sexual activity.
Treatments
A sample of bodily fluid will be taken for cultures in a lab. Tests may also be done for other sexually transmitted infections that commonly occur at the same time as gonorrhea.
Antibiotics are prescribed for treatment. Because drug-resistant strains of bacteria are becoming common, it is extremely important that you finish all of the antibiotics and see the doctor again if your symptoms persist after treatment.
Visit Urgency
- There is a discharge from the vagina, penis, or rectum.
- There is burning or pain during urination or defecation.
- You are concerned or know that a sexual partner has similar symptoms or has been diagnosed with gonorrhea.
Trusted Links
References
>Bolognia, Jean L., ed. Dermatology, pp.1282-1287. New York: Mosby, 2003.
Freedberg, Irwin M., ed. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 6th ed, pp.1105, 2205-2206, 2208-2209. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003.
Last modified on October 10th, 2022 at 7:07 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder