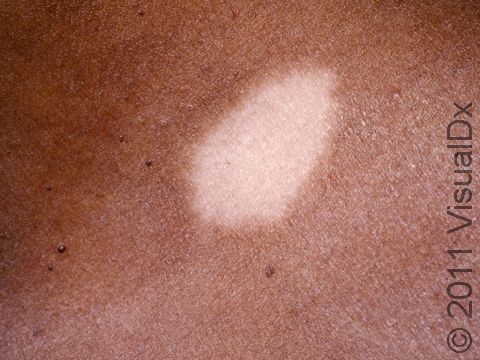
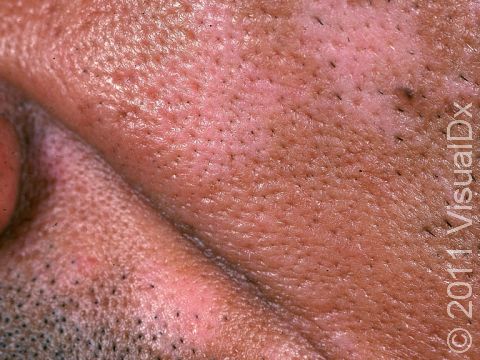
Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation
Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation is a loss of skin color (pigmentation) after your skin heals from an injury. The pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) are damaged or destroyed in the healing process.
Who's At Risk?
Anyone can experience pigment loss, but it is often more prominent in darker-skinned people due to the contrast with their normal skin color. It can occur with any skin injury (burns, cuts, or surgery) or with many skin disorders (acne, eczema, chickenpox, seborrheic dermatitis, and others). Some medications may cause skin lightening in dark-skinned people (eg, strong cortisone creams or benzoyl peroxide products).
Signs & Symptoms
One or more areas of white or lighter areas of skin. The size, shape, and area(s) affected depend upon the cause.
Self-Care Guidelines
Stop any creams or lotions with benzoyl peroxide or strong cortisone. If there are only a few areas and you have no underlying skin problem, no treatment is needed. In mild cases, the skin restores pigment on its own.
Treatments
This will depend upon the diagnosis and cause, and you might need to have a portion of skin taken and checked under a microscope (biopsy) to determine what is causing the discoloration.
Visit Urgency
Seek medical care if you have multiple unexplained, lighter skin areas; if you have a single lighter skin area with no history of previous injury; or if you have a lighter skin area that is numb or has lost sensation or feeling.
Seek medical care if you have any skin condition that leaves multiple lighter skin spots.
Trusted Links
References
Bolognia, Jean L., ed. Dermatology, pp.947-973. New York: Mosby, 2003.
Freedberg, Irwin M., ed. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 6th ed, pp.819, 2141. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003.
Last modified on October 5th, 2022 at 7:50 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder