Myxoid Cyst
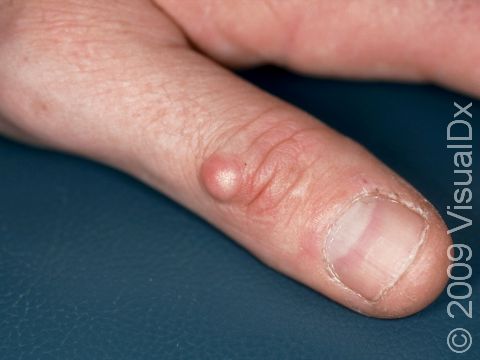
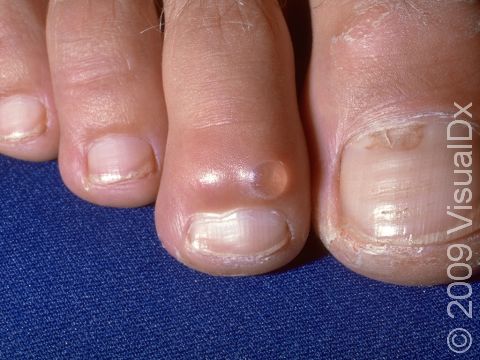
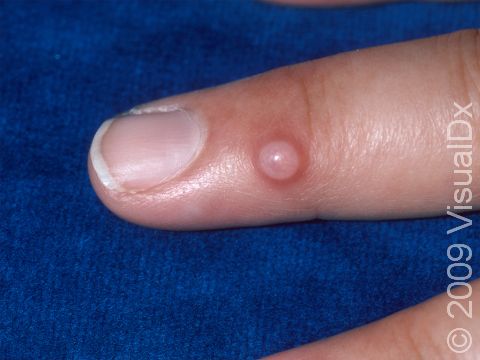
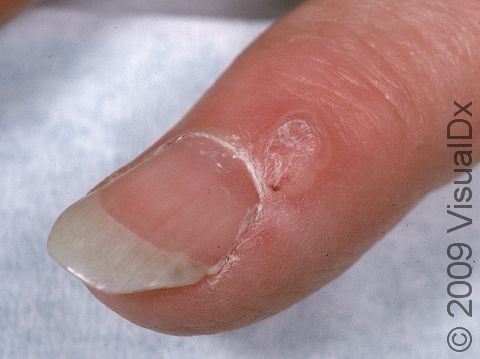
A myxoid cyst, also known as a digital mucous cyst or pseudocyst, is a growth usually occurring on the finger. These cysts are believed to form from deteriorated tissues. Myxoid cysts may be associated with osteoarthritis.
Who's At Risk?
Myxoid cysts are common and are more common in women and the elderly. These lesions occur more frequently on the fingers than on the toes.
Signs & Symptoms
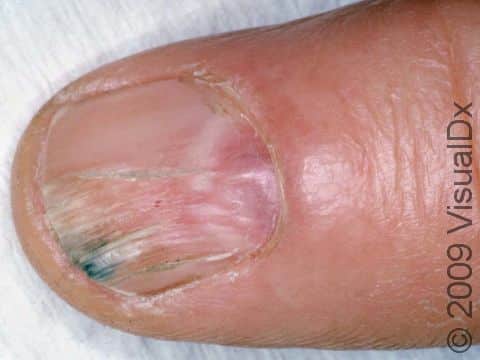
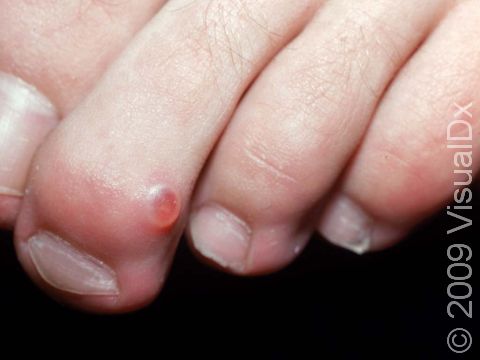
The most common location for myxoid cysts is the fingers. They are usually found near the base of the nail, slightly off to one side or the other. Occasionally, myxoid cysts can occur beneath the nail or involve the root of the nail. When this happens, changes in the nail, such as grooves, depressions, or slight color changes, may be seen. Rarely, these cysts involve the fat pad of the fingertip.
The lesion is a solitary, rounded, flesh-colored, or translucent bump or nodule that may feel relatively firm or may feel more fluid-filled (fluctuant). The fluid inside myxoid cysts is thick, sticky, and clear to yellowish in color.
Self-Care Guidelines
None necessary.
Treatments
If the diagnosis is not certain, your physician may recommend further testing, such as an X-ray, ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI.
Some myxoid cysts will disappear spontaneously. Recurrence rates are high. Patients who fail conservative treatment may require referral to a dermatologic or hand surgeon. A number of treatment options are available. These include, most commonly:
- Repeated puncture
- Corticosteroid tape (flurandrenolide)
- Steroid injections (triamcinolone)
- Cryosurgery (freezing)
- Surgical excision
Visit Urgency
Myxoid cysts are benign, but patients may seek treatment if they become unsightly, cumbersome, or painful.
Trusted Links
References
Bolognia, Jean L., ed. Dermatology, pp.1075, 1730, 2325. New York: Mosby, 2003.
Freedberg, Irwin M., ed. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 6th ed, pp.671, 2580. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003.
Last modified on October 5th, 2022 at 7:41 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder