Excessive Sweating (Hyperhidrosis)
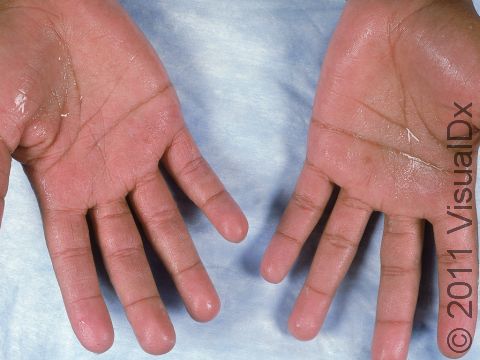
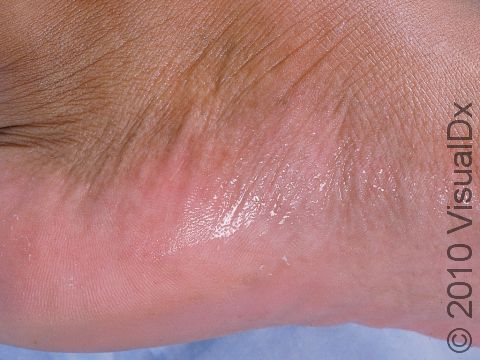
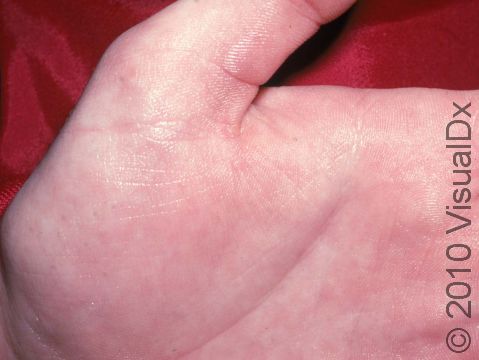
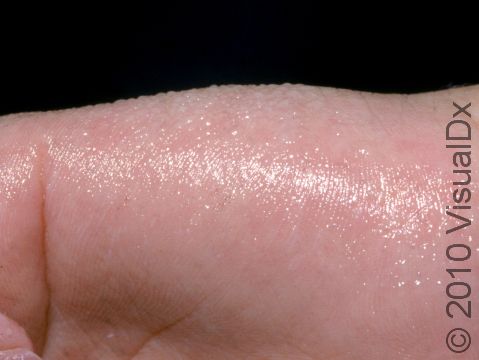
Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating) is a skin condition that most often involves overactive sweat glands of the palms, soles of the feet, or armpits. Sweating can be stimulated through stressful conditions or even with the use of some medications. Soaking sweat through shirts or socks is a common manifestation and can severely affect one’s social interactions. Those who are affected may sometimes avoid touching others, such as avoiding shaking hands, due to embarrassment over this disorder.
Who's At Risk?
Excessive sweating is usually diagnosed in childhood or during the teenage years. It can sometimes first present in adults, but this is less likely. Sometimes there is a family history of excessive sweating.
Signs & Symptoms
Excessive sweating can develop during certain emotional states, such as under stressful conditions, or in association with certain medications.
Self-Care Guidelines
Treatment progress can be made if inciting factors that lead to hyperhidrosis (certain foods, medications, or stressful situations) are identified and avoided. Use of over-the-counter antiperspirants can be helpful to decrease the amount of sweating. New “clinical strength” antiperspirants are now available (Secret®, Dove®) over the counter, which have been helpful for self-treatment. Additionally, there are products designed specifically for use on the feet (Certain Dri® Feet Moisture Control Pads, Certain Dri Feet Microsponge® Powder). Use of antiperspirant/deodorant combinations can help with the prevention of odor. Wearing natural fabrics, like cotton socks, can help to wick moisture away from areas of sweating and allow for faster drying of the skin.
Treatments
There are several common treatments that can be tried to effectively reduce the impact of symptoms of excessive sweating, including the following:
- Topical aluminum compounds (Drysol™, 20% aluminum chloride) – Act by blocking (occluding) the sweat gland.
- Glycopyrrolate – An oral medication that blocks molecules involved in signaling between the nervous system and the sweat glands.
- Oxybutynin – Another oral medication that blocks molecules involved in signaling between the nervous system and the sweat glands.
- Iontophoresis – Involves the passage of electric current into the skin, thereby disrupting the functioning of the sweat glands. This is most easily used for the palms and soles. Home units can be purchased for use within the home.
- Botulinum toxin injection (Botox®) – Used to inhibit signaling between the nervous system and the muscle fibers found in the sweat glands.
- Sympathectomy – A surgical procedure used as a last attempt to get control of symptoms. The nerves of the sympathetic nervous system (those that govern the sweating behavior) are cut to reduce symptoms. Unfortunately, side effects such as excessive sweating in previously unaffected areas (known as compensatory hyperhidrosis) can result.
Visit Urgency
Consultation with a physician should be sought when over-the-counter antiperspirants/deodorants are not effective in controlling symptoms. If symptoms are debilitating, causing major lifestyle changes to avoid developing symptoms or fear or embarrassment, patients should seek consultation with a dermatologist.
Last modified on August 16th, 2022 at 2:45 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder