Bug Bites or Stings, First Aid
Bites or stings from insects (arthropods) are very common. Most reactions are mild and result due to an allergic reaction to either the insect or the toxins injected with the bite or sting. Some people have severe reactions to the stings of:
- Bees
- Wasps
- Hornets
- Yellow jackets
These stings may require emergency help. The bites of most insects – such as ants, mosquitoes, flies, spiders, ticks, bugs, and mites – do not cause such a severe reaction.
Sometimes, it may be hard to tell which type of insect has caused the skin lesions, as many insect reactions are similar. Flying insects tend to bite any exposed skin areas, while bugs such as fleas tend to bite the lower legs and around the waist and often have several bites grouped together. Some individuals are far more sensitive to insects and have more severe reactions, so the fact that no one else in the family has lesions does not rule out an insect bite.
First Aid Guide
For stings:
- Bees may leave a stinger behind – Try to gently scrape off the stinger with a blunt object, such as a credit card.
- Wash the wound with soap and water.
- Apply an ice pack or cold water for a few minutes.
- Take acetaminophen for pain and an antihistamine (diphenhydramine or chlorpheniramine) for itching, as needed.
For insect bites:
- Wash with soap and water.
- Apply cool compresses.
- Use antihistamines to relieve itching and take acetaminophen for pain.
- 1% hydrocortisone cream may help reduce the itching.
For ticks (still attached), see the first aid section on Tick Bites.
Who's At Risk?
Insect bites and stings are a problem in all regions of the world for people of all ages. In the Midwest and East Coast regions of the US, mosquitos, flying insects, and ticks account for most bites. In drier areas of the Western US, crawling insects are more of a problem.
There is no proven effect on race or sex in terms of bite reactions. However, some individuals clearly appear more attractive to insects, perhaps related to body heat, odor, or carbon dioxide excretion.
Severe allergic reactions to stings occur in .5–5% of the US population.
Signs & Symptoms
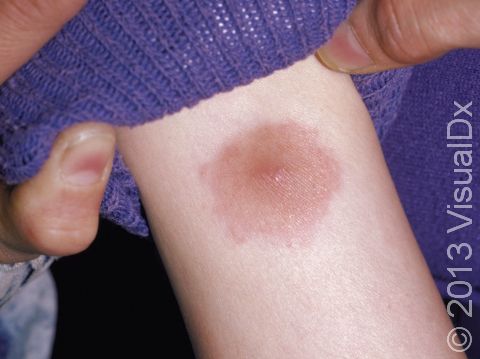
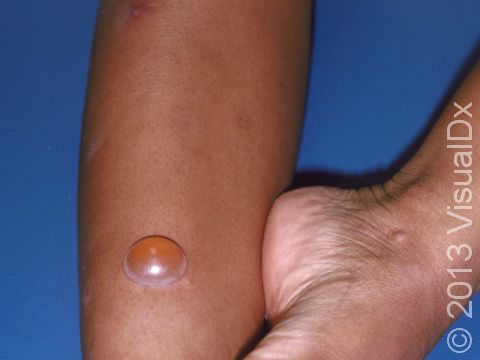
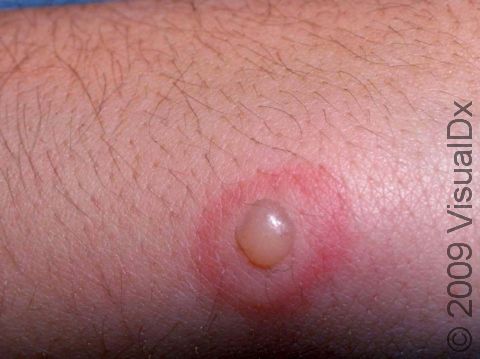
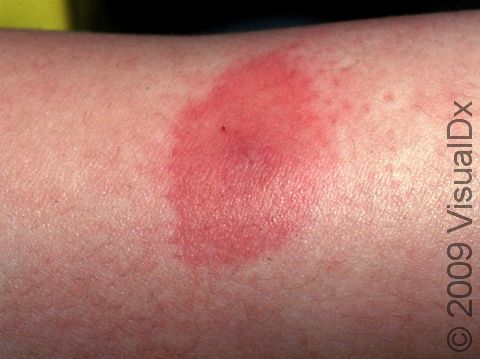
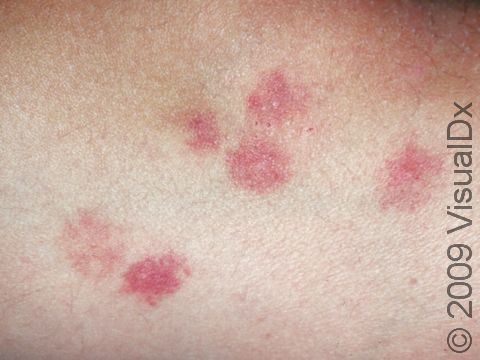
Insect bites usually present as small, itchy red bumps, with the occasional blister occurring. Some insects, such as fire ants, are known to cause a painful, itchy pus-filled bump.
Flying insects tend to choose exposed areas not covered by clothing, while some bugs (such as fleas) focus on the lower legs. Bedbugs prefer the head and neck area, often biting several times in the same area and leaving a group of lesions.
Common reactions to arthropod stings include:
- Redness, pain, and swelling
- Severe reactions such as facial swelling, difficulty breathing, and shock (anaphylaxis)
- Fever, hives, and painful joints (though these reactions are not as common)
Very few spiders cause severe reactions. The black widow spider may cause only a mild local reaction at the bite site, but pain, stiffness, chills, fever, nausea, and abdominal pain may follow within a few hours. Similarly, the brown recluse spider causes a marked skin reaction after a few hours, with redness, pain, blistering, and ulcers forming, as well as fever, nausea, and fatigue.
Treatments
Depending upon the type of insect bite and reaction, your primary care giver might treat you in the following manner.
For insect bites:
- Prescription topical corticosteroids
- Muscle relaxants, pain medicines, antivenin, antibiotics, and sometimes local surgery to relieve venomous insect bites
For stings:
- Antihistamines or corticosteroids
- Epinephrine, antihistamines, corticosteroids, intravenous fluids, and oxygen (for anaphylaxis)
- Injectable epinephrine, for those with known severe allergic reactions
- Immunotherapy to reduce the chance of repeated severe reactions
Visit Urgency
Some arthropod bites/stings are more dangerous than others. If a black widow or brown recluse spider bite is suspected, apply ice to the area and seek medical help. Symptoms of these bites include:
- A deep blue or purple area around the bite, often with a surrounding white area and a red outer ring
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Muscle stiffness
If the site of a tick bite develops a red, swollen, spreading area, seek medical help to check for Lyme disease.
When dealing with stings, be sure to watch out for symptoms such as:
- Hives, itching, or swelling in areas beyond the sting site
- Swelling of the lips or throat
- Tightness in the chest or difficulty breathing
- Hoarse voice or tongue swelling
- Dizziness or loss of consciousness
Last modified on October 6th, 2022 at 2:46 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder