Diabetic Dermopathy
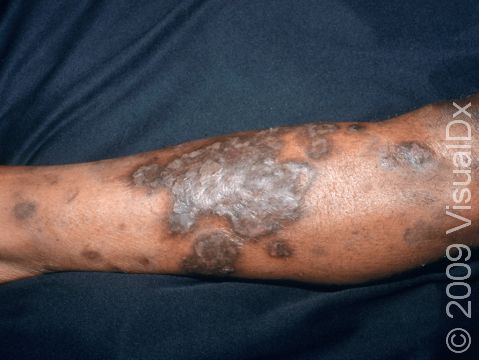
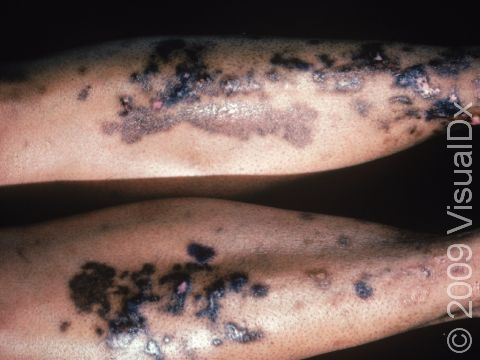
Diabetic dermopathy, also known as shin spots or pigmented pretibial patches, is a skin condition usually found on the lower legs of people with diabetes. It is thought to result from changes in the small blood vessels that supply the skin and from minor leakage of blood products from these vessels into the skin.
Who's At Risk?
Diabetic dermopathy is the most common skin finding in people with diabetes. Up to 50% of diabetics may have shin spots, and it seems to be even more common in people with long-standing or poorly controlled diabetes.
In people who do not have diabetes, the lesions often appear after injury.
Signs & Symptoms
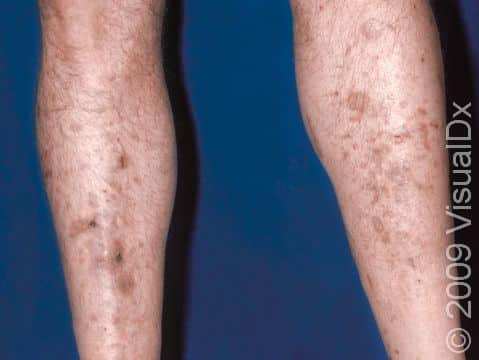
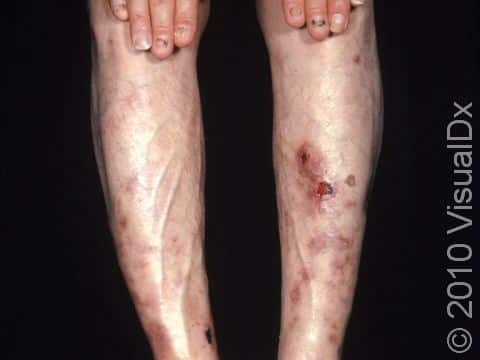
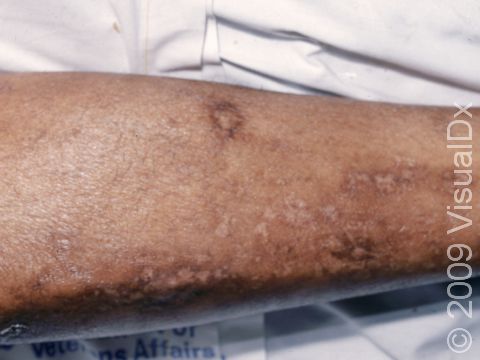
Diabetic dermopathy appears as pink to red or tan to dark brown patches, and it is most frequently found on the lower legs. The patches are slightly scaly and are usually round or oval. Long-standing patches may become faintly indented (atrophic).
Locations of diabetic dermopathy:
- Shins (the pretibial area)
- Thighs
- Sides of feet
- Forearms
Diabetic dermopathy does not typically itch, burn, or sting.
Self-Care Guidelines
The skin lesions of diabetic dermopathy often improve over time. Keeping skin moisturized and trying to avoid any injury to the legs should help prevent the development of some lesions.
Treatments
If necessary, a physician will likely stress the importance of controlling blood sugar and reiterate that appropriate diabetes management will help improve lesions as quickly as possible.
Visit Urgency
Diabetic dermopathy is harmless and does not require any treatment.
Trusted Links
References
Bolognia, Jean L., ed. Dermatology, pp.1653, 1658. New York: Mosby, 2003.
Freedberg, Irwin M., ed. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 6th ed, pp.716. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003.
Last modified on October 10th, 2022 at 7:16 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder