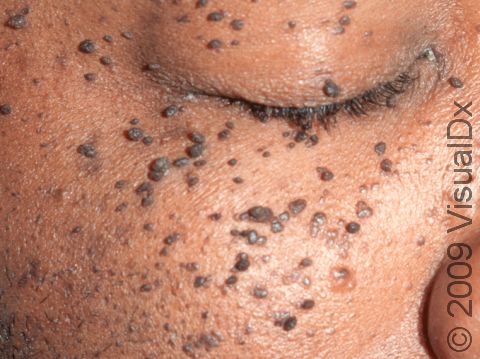
Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra
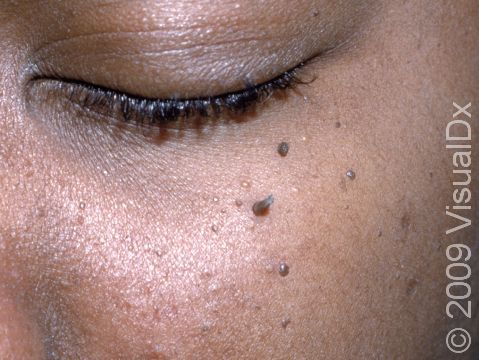
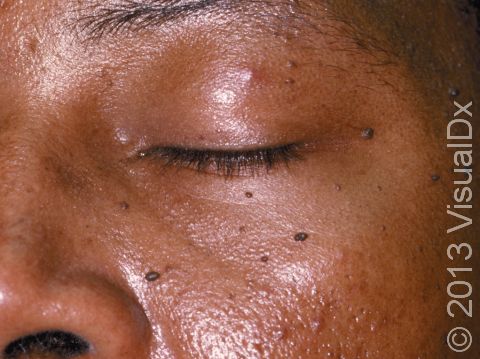
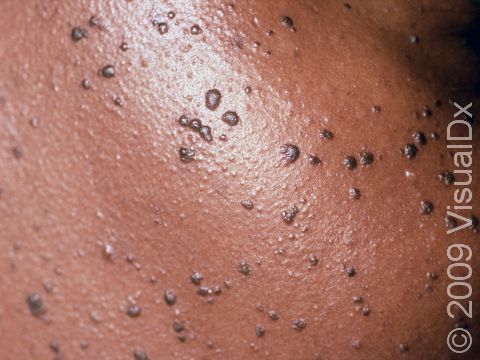
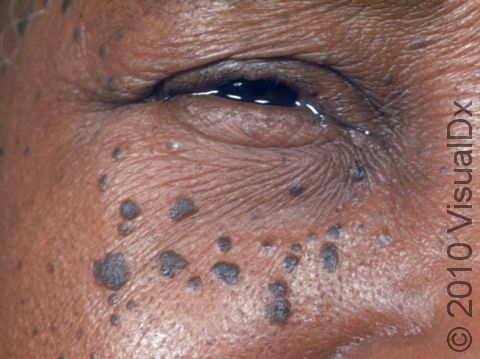
Dermatosis papulosa nigra is a harmless condition commonly affecting the faces of black and sometimes Asian adults. The cause of dermatosis papulosa nigra is unknown, although about half of people affected have a family history of the disease.
Who's At Risk?
Dermatosis papulosa nigra affects up to 35% of people of African descent and an unknown proportion of individuals of Asian descent. Women are affected more than men. Dermatosis papulosa nigra usually begins in adolescence, and the number and size of lesions increase with age. The spots of dermatosis papulosa nigra do not go away.
Signs & Symptoms
Numerous 1–5 mm firm, smooth, raised, dark brown to black bumps occur on the cheeks and forehead. Sometimes these bumps may also be on the neck and trunk.
- Mild – less than 10 spots
- Moderate – 10 to 50 spots
- Severe – more than 50 spots
Self-Care Guidelines
No treatment is needed for dermatosis papulosa nigra lesions unless they are bothersome cosmetically.
Treatments
Freezing (cryosurgery), scraping (curettage), and burning (electrocautery) are all effective removal methods.
Visit Urgency
When removal of dermatosis papulosa nigra lesions is sought, care must be taken to be conservative to avoid scars and loss of pigment in the skin.
Treatment cost is usually not covered by insurance.
Trusted Links
References
Bolognia, Jean L., ed. Dermatology, pp.1701-1702. New York: Mosby, 2003.
Last modified on October 5th, 2022 at 7:19 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder