Cutis Rhomboidalis Nuchae
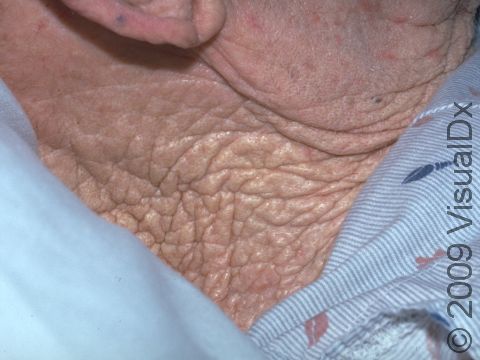
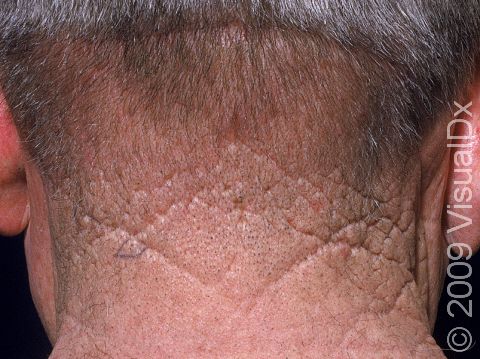
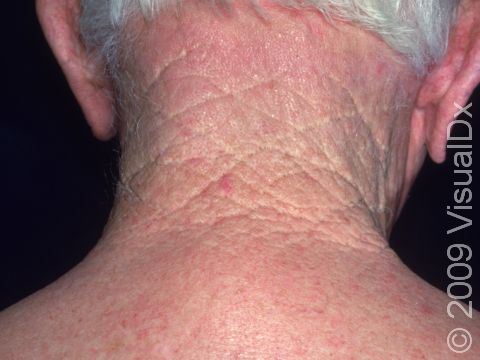
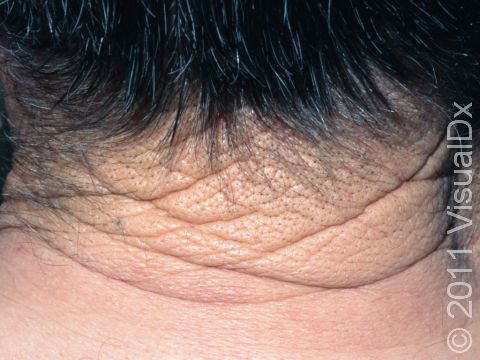
Cutis rhomboidalis nuchae refers to the manifestation of long-term, prolonged sun exposure and resultant damage to the skin occurring on the back of the neck. Long-term, chronic sun exposure causes thickening of the most superficial layer of the skin (the epidermis) and abnormalities in the composition of the middle layer of the skin (the dermis).
Who's At Risk?
Cutis rhomboidalis nuchae occurs in adults, particularly those with a history of prolonged sun exposure.
Signs & Symptoms
Cutis rhomboidalis nuchae appears on the back of the neck as deep wrinkling and furrowing of the skin associated with a leathery texture.
Self-Care Guidelines
For prevention of cutis rhomboidalis nuchae and other signs of sun damage, sun exposure should be avoided midday (10:00 AM to 3:00 PM), sun-protective clothing should be worn (tightly woven clothes and hats), and sunscreen should be applied (SPF 30 UVA and UVB block).
Treatments
No treatment is needed for cutis rhomboidalis nuchae.
Visit Urgency
Cutis rhomboidalis nuchae does not require medical intervention but is a sign of severe sun damage.
Trusted Links
References
Bolognia, Jean L., ed. Dermatology, pp.1380-1381. New York: Mosby, 2003.
Last modified on October 5th, 2022 at 7:15 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder