Mole (Nevus)
A mole (nevus) is a common skin lesion that is made up of the color-producing (pigment-producing) cells of the skin. A mole that is present at birth is referred to as a congenital nevus. A dysplastic nevus, which is discussed elsewhere, is a mole in which unusual (atypical) growth is noted. Moles (nevi, the plural of nevus) slowly enlarge evenly in all directions. After they stop growing (stabilize), they may persist or they may become smaller (regress) later in life. Sun exposure as well as family tendency (heredity) play a role in the development of moles. Moles may sometimes become inflamed or irritated by friction from rubbing or contact with rough clothing or by other types of injury.
Who's At Risk?
Moles may occur in people of all races and ages, but they most commonly appear between the ages of 10 and 30. Light-skinned people are most likely to develop moles.
Signs & Symptoms
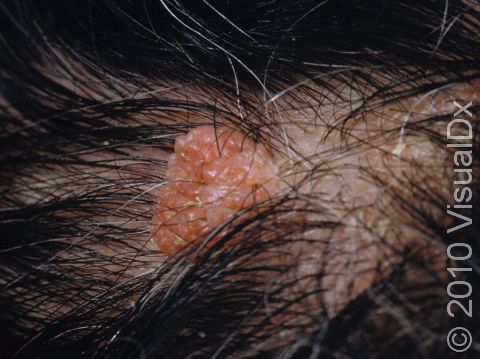
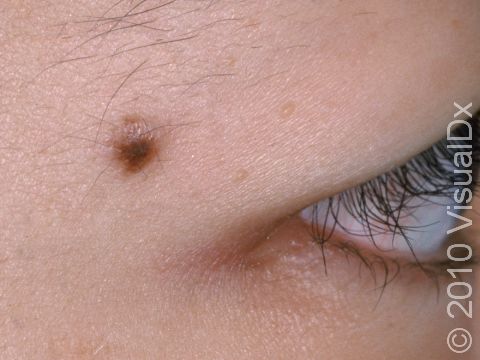
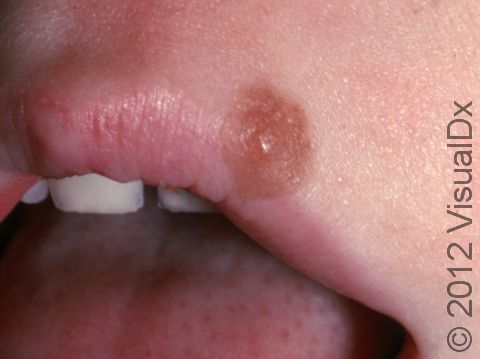
- Moles may occur anywhere on the body, including the nails, palms, and soles.
- Moles may be raised or flat.
- The color of moles may vary from pink to skin colored, to brown, but they may be darker in people with normally darker skin.
- Non-cancerous (benign) moles are usually alike on both sides (symmetrical), have smooth borders and regular color, and they are generally smaller than the size of a pencil eraser (6 mm).
Self-Care Guidelines
- Protective measures, such as avoiding skin exposure to sunlight during peak sun hours (10 AM to 3 PM), wearing protective clothing, and applying high-SPF sunscreen are essential for reducing exposure to harmful ultraviolet (UV) light.
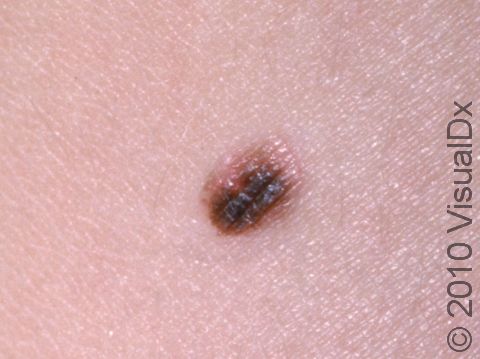
- Monthly self-examination of the skin is helpful to detect new lesions or changes in existing lesions. Be sure your child’s moles are not signs of skin cancer (melanoma). Remember the ABCDEs of melanoma lesions:
A – Asymmetry: One half of the lesion does not mirror the other half.
B – Border: The borders are irregular or vague (indistinct).
C – Color: More than one color may be noted within the mole.
D – Diameter: Size greater than 6 mm (roughly the size of a pencil eraser) may be concerning.
E – Evolving: Notable changes in the lesion over time are suspicious signs for skin cancer.
Treatments
- Non-cancerous (benign) moles do not require treatment, though they may be cosmetically removed.
- If benign-appearing moles are inflamed or irritated, they can be surgically removed.
Visit Urgency
- People with multiple moles and unusual (atypical) moles should be examined by a dermatologist every 4–12 months depending on their past history and family history.
- It may be difficult to tell an atypical mole from a normal mole, so seek medical evaluation for your child if you are unsure about the nature of a mole, if you note changes within a mole, or if a mole becomes irritated or painful.
Trusted Links
References
eedberg, Irwin M., ed. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 6th ed. pp.889-893. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003.
Last modified on February 10th, 2023 at 6:54 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder